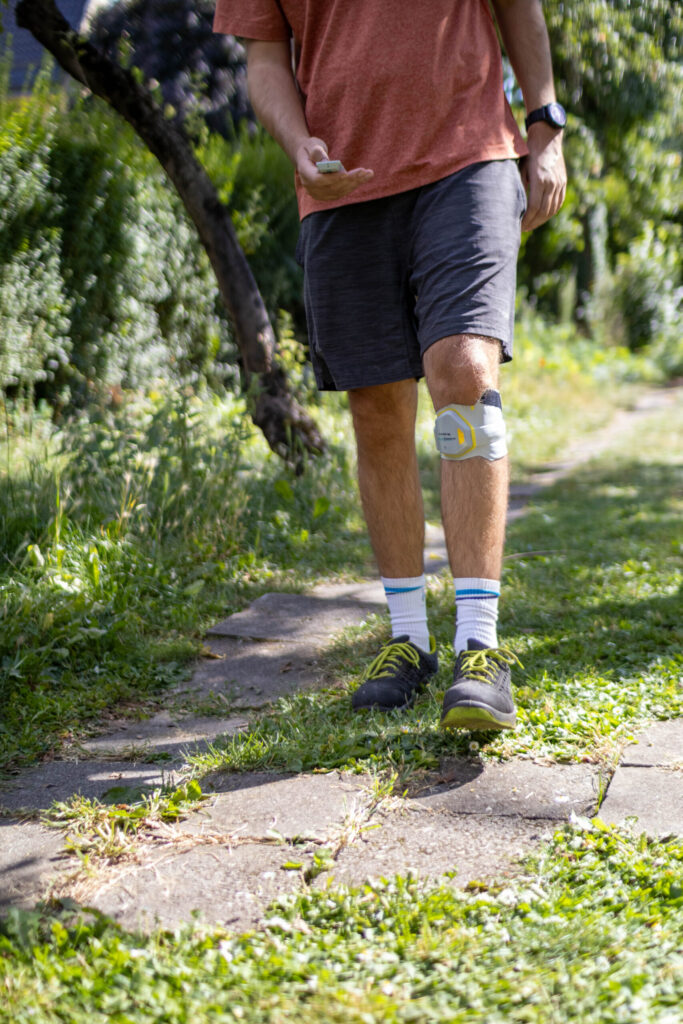
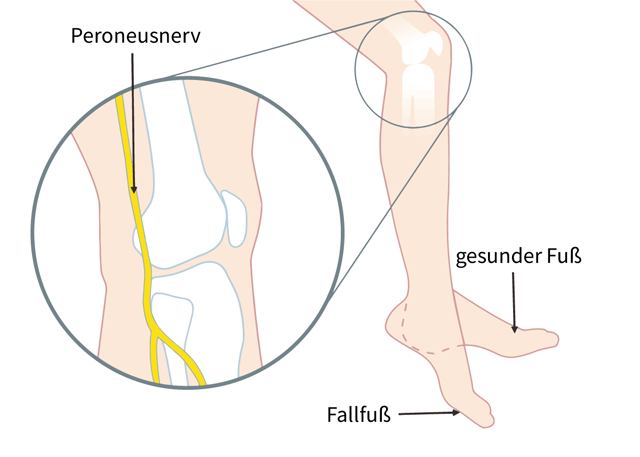
Peroneal compression/entrapment: often good recovery after pressure relief; months.
L5 radiculopathy: course depends on cause (prolapse vs. stenosis); clarify neurosurgically if deficit persists.
Central causes (e.g. stroke, MS): structurally persistent, functionally often partially compensated by neurorehab/FES.